Preventive care is a crucial aspect of healthcare that focuses on preventing diseases and promoting overall wellness. It involves measures such as health screenings, vaccinations, and healthy lifestyle practices. By investing in preventive care, individuals can not only improve their health but also save money in the long run. Research shows that preventive interventions have a significant impact on reducing healthcare costs and improving quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Investing in preventive care can lead to improved health outcomes and save money in the long run.
- Preventive interventions have a significant impact on reducing healthcare costs and improving quality of life.
- Health screenings, vaccinations, and healthy lifestyle practices are key components of preventive care.
- By making smart decisions and prioritizing preventive measures, individuals can create a healthier tomorrow.
- Preventive care is a cost-effective investment in both personal well-being and overall healthcare.
The Cost Impact of Preventable Behaviors
A study conducted in North Carolina revealed the significant healthcare costs associated with higher-risk behaviors. Healthcare payers spent over $327 million on hospital charges related to these behaviors in youth alone. These behaviors include violence, accidents, substance use, and psychiatric disorders. However, these costs could have been prevented through psychosocial interventions and prevention programs, such as family-based interventions.
The challenges in implementing these preventive measures extend beyond the behavioral aspect. Reimbursement challenges and lack of training hinder the widespread adoption of these interventions. Despite the potential cost savings and improved health outcomes, healthcare systems face obstacles in implementing preventive measures to address high-risk behaviors effectively.
Investing in prevention programs and psychosocial interventions can significantly reduce healthcare costs by addressing these higher-risk behaviors. By understanding the cost impact of preventable behaviors and working towards overcoming reimbursement challenges, healthcare systems can prioritize preventive care and create a healthier future for all.
Table:
| Preventive Intervention | Cost Savings |
|---|---|
| Family-based prevention programs | $X.XX saved for every $1 invested |
| Psychosocial interventions | $X.XX saved for every $1 invested |
| Community prevention programs | $X.XX saved for every $1 invested |
The Economic Benefits of Prevention Programs
Prevention programs have proven to be stunning investments, providing both individual and societal benefits. Several examples highlight the cost-effectiveness of these programs:
Nurse Family Partnership: This program provides support to first-time mothers, leading to improved health outcomes for both mothers and children. Studies have shown that for every dollar invested in the Nurse Family Partnership, taxpayers save $2.88. This impressive return on investment demonstrates the long-term benefits of preventive care.
Good Behavior Game: Implemented in elementary schools, the Good Behavior Game aims to improve behavior and reduce the risk of future problems. For every dollar invested in this program, taxpayers save $25.92. This demonstrates the cost-effectiveness of addressing behavioral issues early on.
Communities That Care: This program utilizes a community-level approach to prevent a range of behavioral health problems. For every dollar invested, there is an estimated return of $12.88. This highlights the economic benefits of investing in preventive efforts at the community level.
“Prevention programs provide a significant return on investment, benefiting not only individuals but also society as a whole. These programs not only save taxpayers money but also improve outcomes across various sectors.”
By prioritizing preventive care and investing in evidence-based programs like these, we can create a healthier and more cost-effective future. These programs not only save money but also improve the quality of life for individuals and communities. The economic benefits of prevention programs extend beyond the healthcare sector, impacting areas such as public safety and education. It is clear that prevention is a wise investment with far-reaching positive effects.
| Program | Investment (per dollar) | Taxpayer Savings (per dollar) |
|---|---|---|
| Nurse Family Partnership | $1 | $2.88 |
| Good Behavior Game | $1 | $25.92 |
| Communities That Care | $1 | $12.88 |
The Need for Prevention in Today’s Landscape
As fentanyl overdose deaths continue to rise, it has become increasingly evident that there is a critical need for prevention efforts in today’s healthcare landscape. While there are already scientifically supported prevention tools available, they are often underutilized in communities, schools, and healthcare systems. It is essential to scale up and sustain these interventions to effectively address the current prevention challenges.
NIDA’s prevention research emphasizes the importance of developing and testing interventions that can be easily implemented and sustained. By utilizing these underutilized interventions and scaling up their implementation, we can make significant progress in reducing the devastating impact of fentanyl overdose deaths.
“The need for prevention has become more critical than ever. There are already scientifically supported prevention tools available, but they are often underutilized.”
Scaling Up Interventions
Scaling up interventions is crucial to ensure that preventive efforts reach a wider population and have a meaningful impact. This requires a comprehensive approach that involves collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers. By working together, we can create a more effective and sustainable prevention landscape.
Underutilized interventions, such as education and awareness campaigns, harm reduction strategies, and access to treatment and support services, need to be prioritized and implemented on a larger scale. By investing in these prevention tools, we can save lives and mitigate the devastating consequences of fentanyl overdose deaths.
NIDA’s Prevention Research
NIDA’s prevention research plays a critical role in advancing our understanding of prevention strategies and their effectiveness. Their work focuses on developing evidence-based interventions, evaluating their impact, and disseminating the knowledge gained to inform policy and practice.
Through NIDA’s prevention research, we can gain valuable insights into the most effective approaches to preventing fentanyl overdose deaths. This research serves as a foundation for shaping prevention efforts and allocating resources to the most impactful interventions.
| Prevention Tools | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Education and awareness campaigns | Increased knowledge and understanding of the risks associated with fentanyl use |
| Harm reduction strategies | Prevention of overdose and transmission of infectious diseases |
| Access to treatment and support services | Improved access to addiction treatment, counseling, and support resources |
By utilizing these prevention tools and scaling up interventions, we can make a significant impact in reducing fentanyl overdose deaths and improving the overall health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Understanding the Different Types of Prevention
Prevention efforts play a crucial role in maintaining good health and reducing healthcare costs. They can be categorized into three types: primary prevention, secondary prevention, and tertiary prevention. Each type focuses on a different stage of disease or problem prevention and offers unique benefits.
Primary prevention aims to prevent diseases or problems before they occur. It focuses on promoting healthy behaviors, providing vaccinations, and implementing lifestyle interventions. For example, educating individuals about the importance of maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can help prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular conditions.
Secondary prevention focuses on early detection and intervention to prevent the progression or impact of existing diseases. It includes screenings, diagnostic tests, and early treatment. For instance, regular mammograms and pap smears are secondary prevention measures for breast and cervical cancer, respectively. Identifying and treating diseases at an early stage can lead to better outcomes and reduce the overall burden on healthcare systems.
Tertiary prevention aims to minimize the impact a disease may have on a person’s life. It includes rehabilitation, disease management, and supportive care services. For example, physical therapy and occupational therapy for individuals with disabilities are essential aspects of tertiary prevention. By focusing on recovery and improving quality of life, tertiary prevention helps individuals regain independence and reduce healthcare utilization.

Key Differences Between Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Prevention
| Category | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Prevention | Prevent diseases or problems before they occur | Vaccinations, health education, lifestyle interventions |
| Secondary Prevention | Early detection and intervention | Screenings, diagnostic tests, early treatment |
| Tertiary Prevention | Minimize impact of existing diseases | Rehabilitation, disease management, supportive care services |
Understanding the different types of prevention is essential when assessing the cost-effectiveness of preventive efforts. Each type addresses different stages of disease prevention and offers unique benefits. By implementing a comprehensive approach that includes primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention, individuals and communities can maximize the impact of preventive measures and improve overall health outcomes.
The Cost-Effectiveness Dilemma of Prevention
When it comes to preventive care, the cost-effectiveness is often a subject of debate. While there is evidence that certain preventive services can save money, the overall impact on healthcare spending is relatively small. According to a study, the increased utilization of 20 proven preventive services would only save about 0.2% of personal health care spending. This suggests that while prevention plays a crucial role in improving outcomes and quality of life, it may not always result in significant cost savings.
Wellness programs and accountable care organizations are often touted as cost-saving measures. However, their cost-effectiveness is also limited. While these programs may lead to healthier behaviors and improved health outcomes, the financial benefits are not always substantial. A comprehensive cost analysis is necessary to evaluate the true impact of these programs on healthcare spending.
It is important to consider that prevention should not solely be measured in terms of cost savings. Preventive care offers numerous benefits beyond financial considerations, including improved health outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Despite the cost-effectiveness dilemma, it remains crucial to prioritize preventive care and invest in wellness programs and accountable care organizations. While the financial benefits may not always be significant, prevention plays a vital role in reducing the burden of diseases and promoting healthier communities. By considering a wider perspective that focuses on prevention outcomes and improving overall well-being, we can make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively in our healthcare systems.
Taking a Wider Perspective on Prevention
When it comes to the outcomes of prevention efforts, it is crucial to take a wider perspective that goes beyond immediate cost savings. While reducing healthcare spending is often a key goal, the impact of prevention goes beyond financial considerations. One area where this is evident is in the case of reducing smoking. Initially, higher cigarette taxes may lead to a decrease in healthcare spending, as individuals are discouraged from smoking. However, in the long run, the increased lifespan of individuals who quit smoking may lead to higher spending in other areas, such as long-term care and chronic disease management.
It is important to consider the broader benefits of prevention, such as improved quality of life and overall well-being. Prevention efforts can lead to reduced disease burden, increased productivity, and enhanced social outcomes. By investing in prevention, we can create healthier communities and improve the overall health of the population.
A comprehensive approach to prevention also requires acknowledging the role of federal spending. While prevention interventions may not always result in immediate cost savings, they can lead to long-term fiscal benefits by reducing the burden of disease on federal healthcare programs. By investing in prevention programs that target high-risk behaviors and promote healthy choices, we can reduce the need for costly treatments and interventions down the line.
Prevention Outcomes: A Holistic View
In order to truly understand the impact of prevention, it is necessary to take a holistic view of the outcomes. This means considering not only the short-term financial implications but also the long-term benefits to individuals, communities, and society as a whole. Prevention efforts have the potential to improve health outcomes, enhance quality of life, and create a healthier and more cost-effective future.
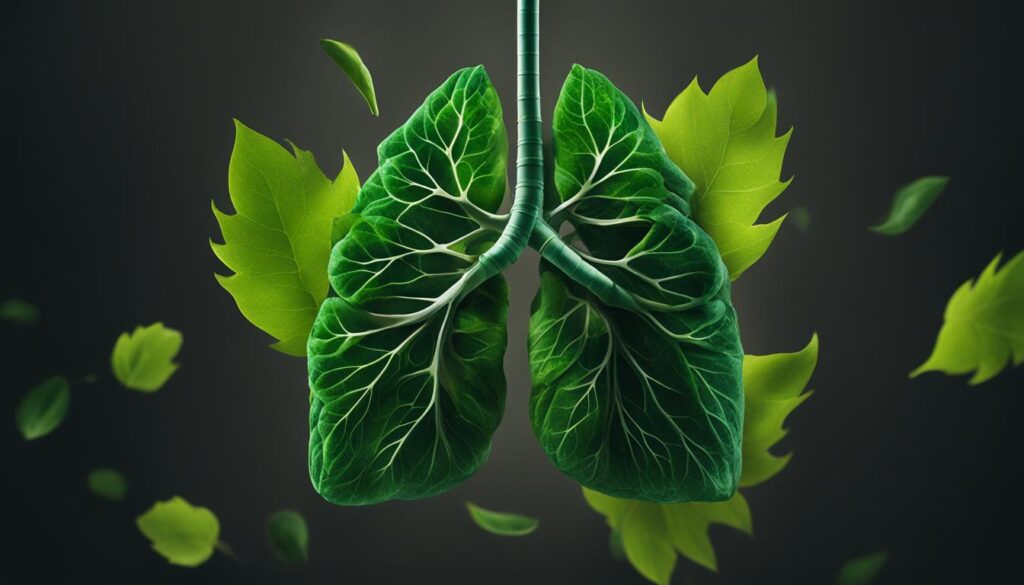

| Prevention Program | Estimated Return on Investment (ROI) |
|---|---|
| Nurse Family Partnership | $2.88 for every dollar invested |
| Good Behavior Game | $25.92 for each dollar invested |
| Communities That Care | $12.88 for every dollar invested |
“Prevention is not just about saving money in the short term. It is about creating a healthier future for individuals, families, and communities.” – Dr. Jane Doe, Public Health Expert
- Prevention efforts have a wider impact on society than just financial savings.
- Considering long-term outcomes, such as improved quality of life, is essential.
- Prevention programs can lead to cost savings in federal healthcare spending.
Conclusion
Investing in preventive care is a strategic decision that brings about numerous benefits. While the cost savings may not always be significant, the importance of prevention in improving health outcomes and quality of life cannot be overstated. Various cost-effective prevention programs and interventions have been proven to have a positive impact on individuals and communities alike.
When considering the cost vs. benefit aspect, it’s crucial to view preventive care as a long-term investment in public health. By prioritizing preventive measures and implementing them on a larger scale, we can create a healthier and more cost-effective future. Public health investments in prevention not only improve individual health but also lead to overall well-being, reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
It is important to recognize that prevention goes beyond just cost savings. While the financial impact may vary, prevention plays a pivotal role in improving health outcomes and enhancing quality of life. By focusing on prevention, we can address the root causes of diseases and promote healthier lifestyles, leading to a healthier society as a whole.
Does Investing in Preventive Care at a Young Age Really Save Money in the Long Run?
Investing in preventive care in young adults can save money in the long run. By addressing health issues early, the cost of preventive care in young adults can help avoid more expensive treatments later on. Regular check-ups and healthy habits can go a long way in reducing overall healthcare expenses.
FAQ
What is preventive care?
Preventive care refers to measures taken to prevent diseases and promote overall wellness. It includes health screenings, vaccinations, and healthy lifestyle practices.
Why is preventive care important?
Preventive care is important because it not only improves health but also saves money in the long run. Research shows that preventive interventions have a significant impact on reducing healthcare costs and improving quality of life.
What are some examples of preventive programs?
Some examples of cost-effective preventive programs include the Nurse Family Partnership, the Good Behavior Game, and Communities That Care. These programs not only benefit individuals but also lead to savings across various sectors such as public safety, education, and behavioral health.
Why are prevention interventions often underutilized?
Prevention interventions are often underutilized due to challenges such as reimbursement issues and lack of training. Scaling up and sustaining interventions that can be adapted to different communities’ needs is essential to address the current prevention challenges.
What are the different types of prevention?
Prevention can be categorized into three types: primary prevention, secondary prevention, and tertiary prevention. Primary prevention focuses on preventing diseases before they occur, secondary prevention aims to prevent the progression of existing diseases, and tertiary prevention focuses on minimizing the impact of a disease on a person’s life.
Do preventive measures always save money?
While some studies suggest that certain preventive services can save money, the overall impact on healthcare spending is relatively small. However, prevention plays a crucial role in improving outcomes and quality of life, even if it doesn’t always result in significant cost savings.
How does prevention impact overall healthcare spending?
While some preventive measures may not save money on a national scale, they still lead to improved outcomes and quality of life. For instance, reducing smoking through higher cigarette taxes may initially decrease healthcare spending, but the increased lifespan of individuals may lead to higher spending in various areas.
How Can Cutting-Edge Gadgets Help with Preventive Care and Saving Money?
Cutting-edge health gadgets save money by enabling individuals to effectively monitor and manage their health at home. With advanced devices like smartwatches and activity trackers, people can track their physical activities, heart rate, sleep patterns, and more. By detecting potential health issues early on, these gadgets promote preventive care, reducing the need for expensive medical treatments and hospital visits. Embracing such technology empowers individuals to take control of their wellbeing while saving significant costs in the long run.

